Equation-Based Object-Oriented Modeling and Simulation for Data Center Cooling: A Case Study
Data center cooling accounts for about 1% of electricity usage in the United States. Computer models are pivotal in designing and operating energy-efficient cooling systems. Compared to conventional building performance simulation programs, the equation-based object-oriented modeling language Modelica is an emerging approach that can enable fast modeling and dynamic simulation of cooling systems.
In this case study, we first modeled the cooling and control systems of an actual data center located in Massachusetts using the open-source Modelica Buildings library, and then calibrated a baseline model based on measurement data. The simulation of the baseline model identified several operation-related issues in the cooling and control systems. Afterwards, we used a sequential search technique as well as an optimization scheme to investigate the energy saving potentials for different energy efficiency measures. Simulation results show potential energy savings up to 24% by resolving identified control-related issues and optimizing the supply air temperature.
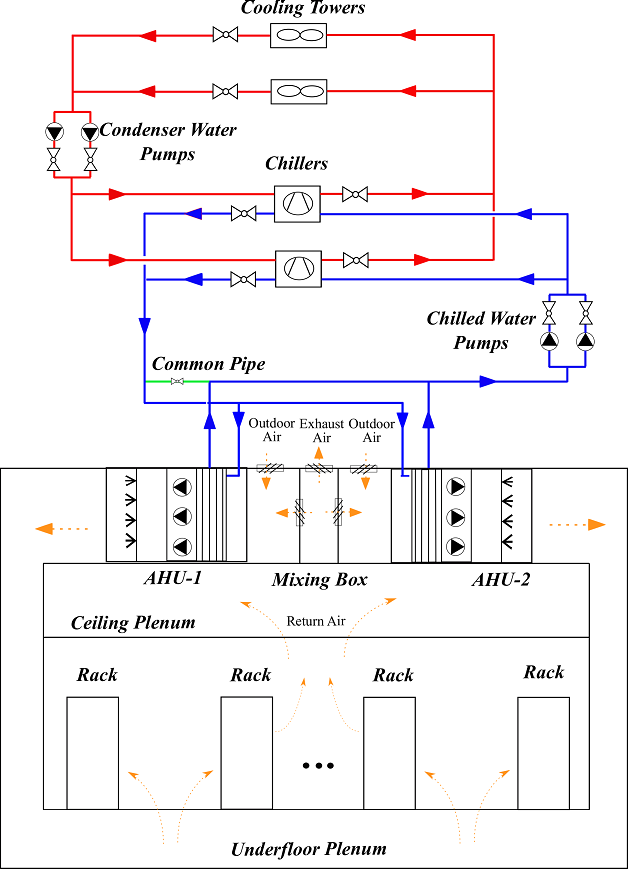
Fig.1 - Diagram of the HVAC system
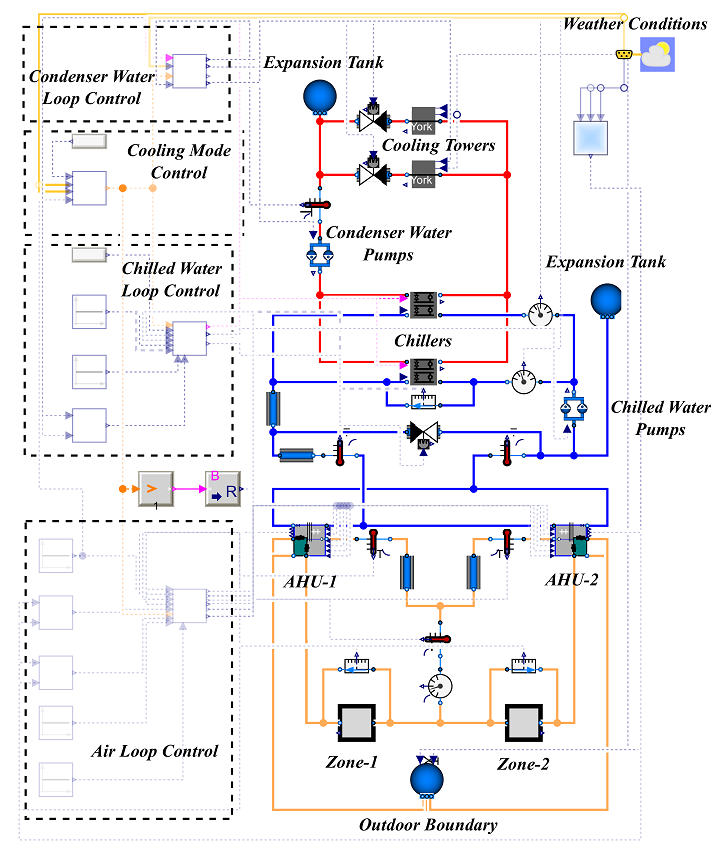
Fig.2 - Modelica model of the HVAC system


Factsheet
| Number of buildings | 1 |
| Number of thermal zones (per building) | 2 |
| Complexity of thermal zone model | High Order |
| Coupling/Decoupling between district network and buildings | - |
| Simulation tool | Dymola |
| Modelica libraries | Buildings |
| Additional packages/workflows/scripts | - |
| Simulation time | One year |
| Computational time | 8 min |
| Solver and tolerance | Dassl / 1e-6 |
| CPU speed | 2.8 GHz |
Authors:
Xu Han (University of Colorado at Boulder - USA)
Yangyang Fu (University of Colorado at Boulder - USA)
Wangda Zuo (University of Colorado at Boulder - USA)
Michael Wetter (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory - USA)
Jim W. VanGilder (Schneider Electric - USA)
David Plamondon (University of University of Massachusetts Medical School - USA)
Xu Han (University of Colorado at Boulder - USA)
Yangyang Fu (University of Colorado at Boulder - USA)
Wangda Zuo (University of Colorado at Boulder - USA)
Michael Wetter (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory - USA)
Jim W. VanGilder (Schneider Electric - USA)
David Plamondon (University of University of Massachusetts Medical School - USA)
References:
Y. Fu, W. Zuo, M. Wetter, J. W. VanGilder, X. Han and D. Plamondon. Equation-based object-oriented modeling and simulation for data center cooling: A case study. Energy and Buildings 186: 108-125, 2019.
Y. Fu, W. Zuo, M. Wetter, J. W. VanGilder, X. Han and D. Plamondon. Equation-based object-oriented modeling and simulation for data center cooling: A case study. Energy and Buildings 186: 108-125, 2019.
