5th generation district heating and cooling (5GDHC) systems are an emerging technology that can contribute to the decarbonization of the heating and cooling sector in cities and communities thanks to their ability to exploit a multitude of renewables and urban excess heat sources.
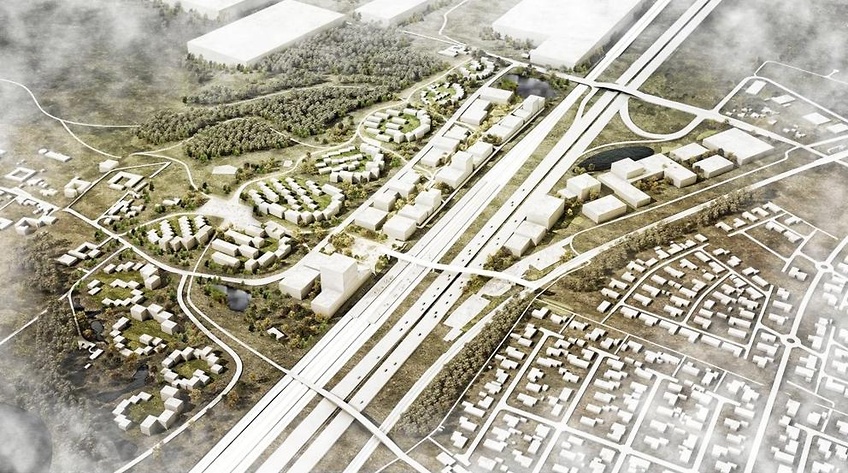
The objective of this case study is to assess the technical feasibility of a 5GDHC system in the new urban area of Køge Nord (Denmark). When fully developed, the area will consist of approximately 15 large office buildings and 60 residential buildings and 3 industrial buildings.
The concept of the system is illustrated in Fig.1. The district piping network consists of two pipes. The warmer pipe has temperatures between 12°C and 20°C, while the cold pipe has 8-16°C. The district network uses aquifer thermal energy storage (ATES) technologies as long-term source/sink to provide heating and cooling to buildings. Buildings are equipped with decentralized “prosumer” substations including heat pumps, direct-cooling heat exchangers and circulations pumps, and they are connected to both lines. In the case of a heating demand, the circulation pump withdraws water from the warm pipe, uses it in a heat pump to reach temperatures suitable for space heating (and/or DHW), and then discharges the cooled water to the cold line. In case of a cooling demand, the system works in the other direction. Depending on the heating and cooling demands of the connected buildings, the fluid flow in the network can change direction. The total difference between heating and cooling flows needs to be balanced by the ATES system. This project started only recently, therefore no results are available.
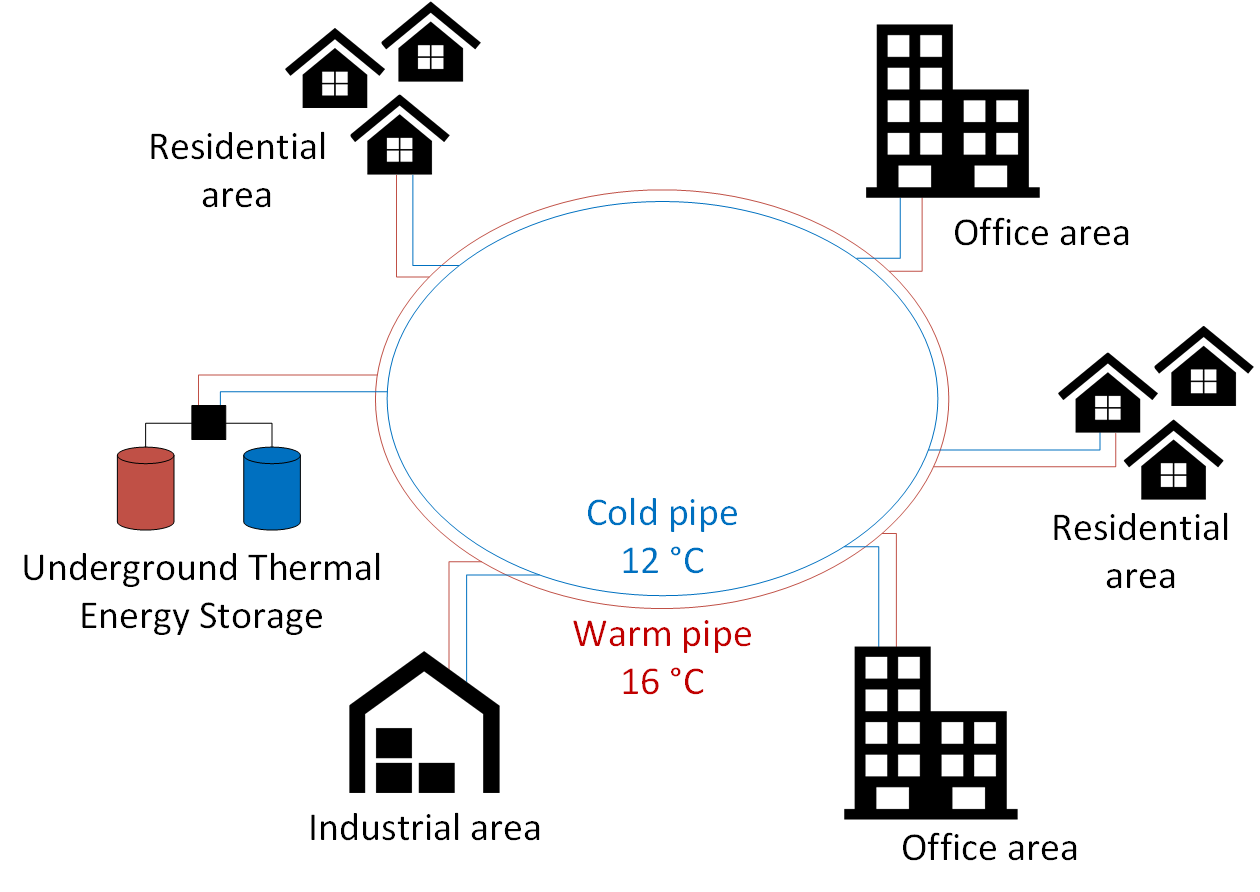 Fig.1 - Layout of the district network
Fig.1 - Layout of the district network



